Blocks
SiteBox Framework works with the Gutenberg editor out of the box. One of Gutenberg's most important paradigms is editing content in block-based structure. Blocks are simply a components oriented on deliverying a complete functionality with its configuration pane and ability to modify a content, visually, on-screen just as it is edited. Such approach is called as What You See Is What You Get (WYSIWYG) and it replaces the traditional concept of freeform text with embedded media and shortcodes - Block Editor Handbook.
SiteBox Blocks Library
Due to a decoupled architecture of SiteBox websites, blocks need to be prepared to be consumed by both back-end and front-end experience separately. Therefore, SiteBox framework comes with a bundled set of blocks, maintained and developed by a dedicated team. It consists of core blocks, which reflects all changes from original blocks released with Gutenberg updates, as well as bespoke blocks to focus on more complex challenges of modern web development for corporate clients and business in general. The team were supposed to address the following issues when developing a dedicated blocks libary:
- Deliver blocks with a long term support so our partner agencies could maintain website for years, any applied changes, even to core blocks, will treat backwards compatibility as a priority,
- Deliver blocks with a support for back-end and front-end experience at the same time. On top of a regular Gutenberg instance of a block, they are delivered with an additional layer of React.js components to handle the front-end experience properly so as a result it could be easily used in Gatsby powered applications,
- Deliver blocks with a unified development experience to let developers update a single codebase for both back-end and front-end experience.
Blocks Architecture
SiteBox Block Library or any other SiteBox compatible block library follow the structure of regular Gutenberg blocks.
Additionaly, to align with a decoupled arichtecture, they come with an
additional React.js layer for Gatsby front-end experience. From a web developer perspective to use Blocks on Headless
project is required use @gatsby-blocks-statik on frontend instance.
Any SiteBox based project can use more than one blocks library. In fact, we encourage our partner agencies to come up with their own block libraries as reusing components saves a lot of time in the development phase.
Blocks Processing
The SiteBox Framework automatically process SiteBox-enhanced Gutenberg blocks so as a result they are ready to use within a front-end application. All blocks from a SiteBox Blocks Library fully align with WYSIWYG approach making the editing process as easy as in classic PHP-based websites.
For an upcoming read, blocks will be divided into 2 categories which affects how they are processed by the SiteBox Framework
- Dynamic Blocks (or stateful blocks, application rendered blocks) – these blocks are dynamic or complex enough to require at least a state management in the front-end experience (Think about blocks that would require tons of jQuery code to handle interactions in the classic approrach). In the front-end, they will be converted into dynamic React.js components that are hydrated with properties coming from block settings,
- Static Blocks (or Server Side Renderable blocks, Server Side Rendered Blocks, SSR blocks) – these blocks are shipped to the front-end applications as HTML output to improve performance of rendering a website. Paragraphs, buttons, quotes or simillar will be shipped differently to dynamic ones.
The lifecycle
This section describes the complete journey of blocks delivery which starts in the Gutenberg experience and ends in the front-end Gatsby.js application. Assuming, we already took SiteBox-enabled blocks with an additional React.js front-end layer into equation, the lifecycle of such a delivery is divided into 4 phases:
- saving data,
- exposing data,
- consuming data,
- rendering blocks.
Saving data
All post types with Gutenberg editing experience enabled perform additional activities to save blocks data in a
dedicated database space. A hook attached to save_post action (@TBD: filter?) in WordPress, iterates through inserted
blocks to process blocks before saving it to the database. Static blocks are converted into a HTML code and
dynamic blocks are saved as a JSON object of block configuration.
Exposing data
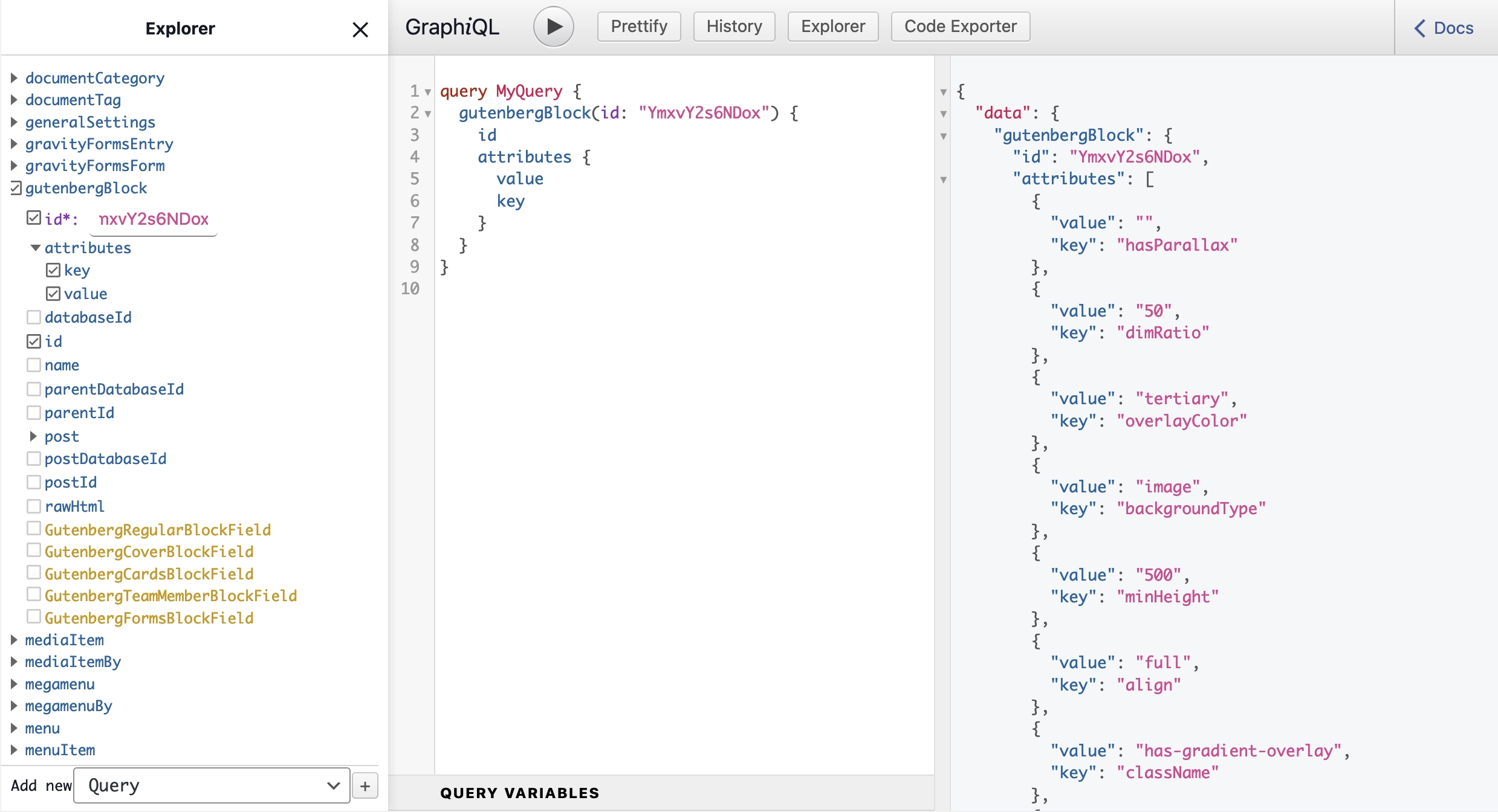
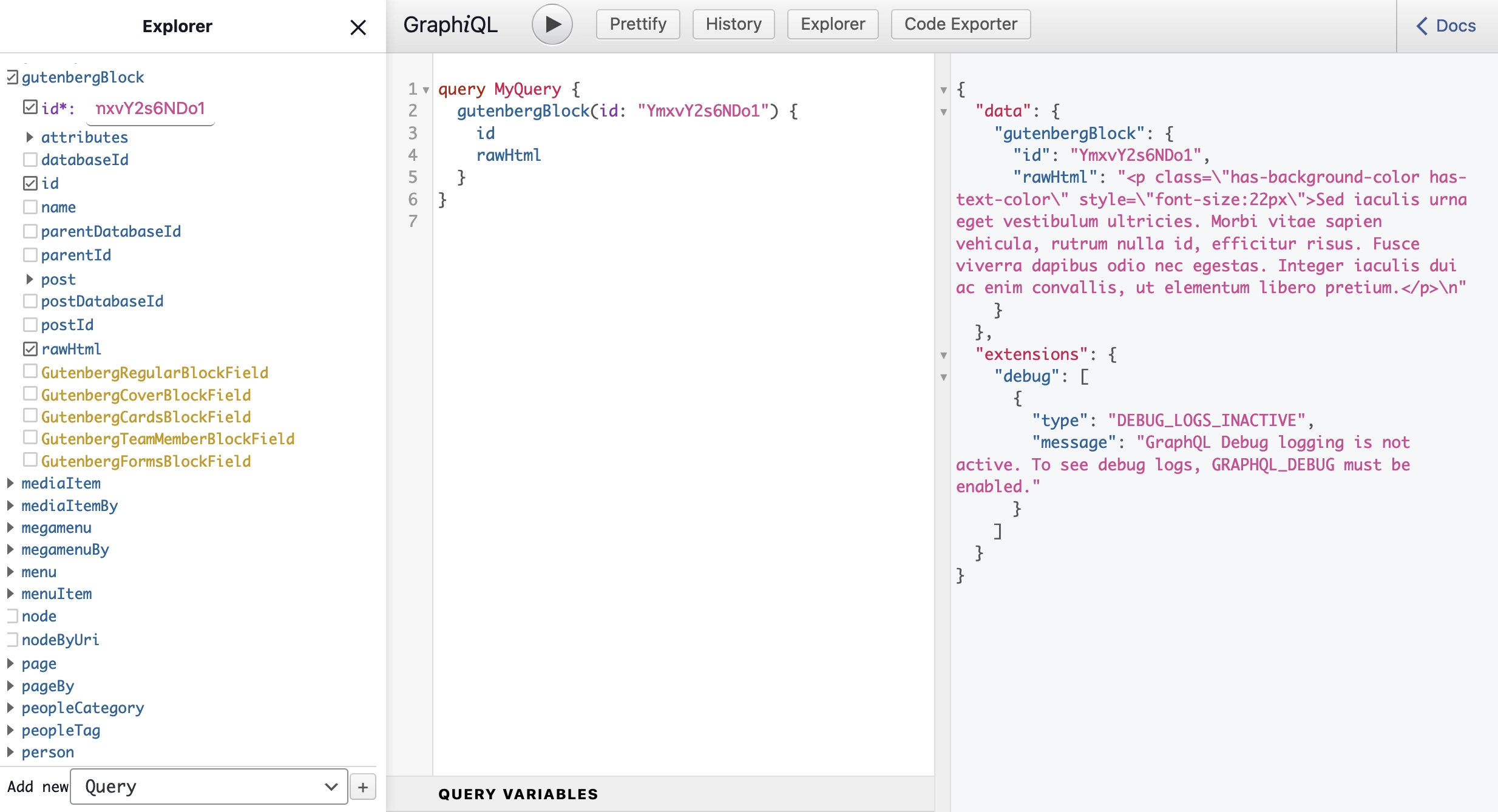
Data saved in a database and then exposed in the GraphQL interface. Static blocks are printed as a raw code in the
rawHtml property, dynamic blocks are printed as a collection of key value pairs in the attributes property. Some
of dynamic blocks are also processed by mutators so the raw data is adjusted to the front-end application needs.
Consuming data
In the front-end application, whenever an output website is built (think about statik build or statik develop
commands), Gatsby runs through a GraphQL interface exposed in the WordPress API and downloads data to its own internal
API, also run on a GraphQL. As a result block data can be easily consumed by pages or collection routes based on project
needs, more about how to use data from an internal Gatsby API is explained on Queries page.
Whenever a specific page or collection route query blocks, the easiest way is to use ...GutenbergBlockFragment
fragment described on Queries page. The GraphQL call will fetch all data that is necessary to render blocks in the
front-end experience, with no further hassle. See the example below, it presents a complete component that fetches
Gutenberg data and prints it on the website.
import React from 'react';
import PropTypes from 'prop-types';
import { graphql } from 'gatsby';
const HelloWorld = props => {
const {
data: {
post: {
title,
gutenbergBlocks,
},
},
} = props;
return (
<main>
<h1>
{gutenbergBlocks && gutenbergBlocks.nodes && (
<StatikBlocks blocks={gutenbergBlocks.nodes} />
)}
</main>
);
};
HelloWorld.propTypes = {
PropTypes.shape({
post: PropTypes.shape({
title: PropTypes.string,
gutenbergBlocks: PropTypes.shape({
nodes: PropTypes.array,
}),
}),
}),
};
export default HelloWorld;
export const query = graphql`
query Query {
post(id: 18) {
title
gutenbergBlocks {
nodes {
...GutenbergBlockFragment
}
}
}
}
`;
Standard Wordpress Projects
When developing a block, remember to prepare separate views for the Gutenberg editor (the backend layer) and for end
users (the frontend layer). If the WordPress Static Blocks package is used in a standard WordPress project, you should
properly prepare the view.js / save.js files. However, if the block is displayed in a headless project (JAM),
preparing the aforementioned files is not necessary. More important is the proper preparation of the data to be sent to
the front-end instance.
View Layer
Static blocks save data that is immediately available for display. They do not require fetching additional data, often from various endpoints.
An example of such a block is the Heading or Paragraph - it saves data and sends it to the front-end view as
rawHtml, meaning that what is sent is immediately available for display.
A more complex example is the Image module. Here, a specific image's id is saved, and based on this id, an element
with a specific identifier must be fetched from the media library. Similarly, blocks responsible for displaying posts
from specific Post Types save data and identifiers of posts that are to be fetched, and are fetched from a separate
endpoint responsible for a specific Post Type.
Save.js/view.js
The save.js/view.js files are responsible for displaying blocks on the front-end. They are not required for projects based on headless CMS.
Save.js
The save.js file is used to define save functions for blocks, which are then used to generate a static HTML structure
that will be saved in the database and displayed on the page.
For static blocks, the content generated by the save function is the same as that displayed on the page. For dynamic
blocks, the save function may only return necessary HTML tags, which will later be supplemented with dynamic content
handled by the view.js file.

For example, the Timeline block contains a Label field, and in the screenshot below, it is not handled in the save.js
file, so it is only sent to the front as an attribute, nested in another block section like Group or Paragraph.

After adding the save.js file for this block, it looks different. You can see the container used to display the
content of the Label field.
View.js
Dynamic blocks require a view.js view. This file is responsible for handling user interactions, animations, dynamic
content loading, initializing external libraries, or any other front-end-specific functionality.
Rendering blocks
As shown on the example above, data fetched through an internal Gatsby API can be rendered thanks to a <StatikBlocks>
component. The collection of blocks delivered in the response can be passed directly to the component. It is then
iterated and based on block type and whether it is known as static or dynamic component, each element is rendered either
by <StaticRenderer> or <DynamicRenderer> internal components.
Please note, only blocks plugged-in as a WordPress and Gatsby extensions will be rendered. Make sure proper library is installed on both ends to display block properly.
<StaticRenderer>
Static renderer is responsible for presenting a raw HTML output. Such payload is obviously processed by side xss libaries to stip out any dangerous code that might potentially impact visitors. As a result, code rendered on a website should be safe to use even before WAF is applied.
<DynamicRenderer>
Dynamic renderer is responsible for mapping a block data with an actual React.js component meant to render it on a website. All block attributes (key value pairs) are injected into the component as properties so they impact the way content is presented.
Neither StaticRenderer or DynamicRenderer should be consumed in
projects. These are internal functions that are automatically called from a
`StaticBlock React.js component.